Overview
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common but potentially dangerous health condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Over time, uncontrolled hypertension can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. With the rising popularity of stimulant medications for treating attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and other conditions, it’s crucial to understand the possible impact of these drugs on blood pressure. In this blog post, we’ll explore the long-term effects of hypertension and the relationship between stimulant medication and blood pressure.
Understanding Hypertension
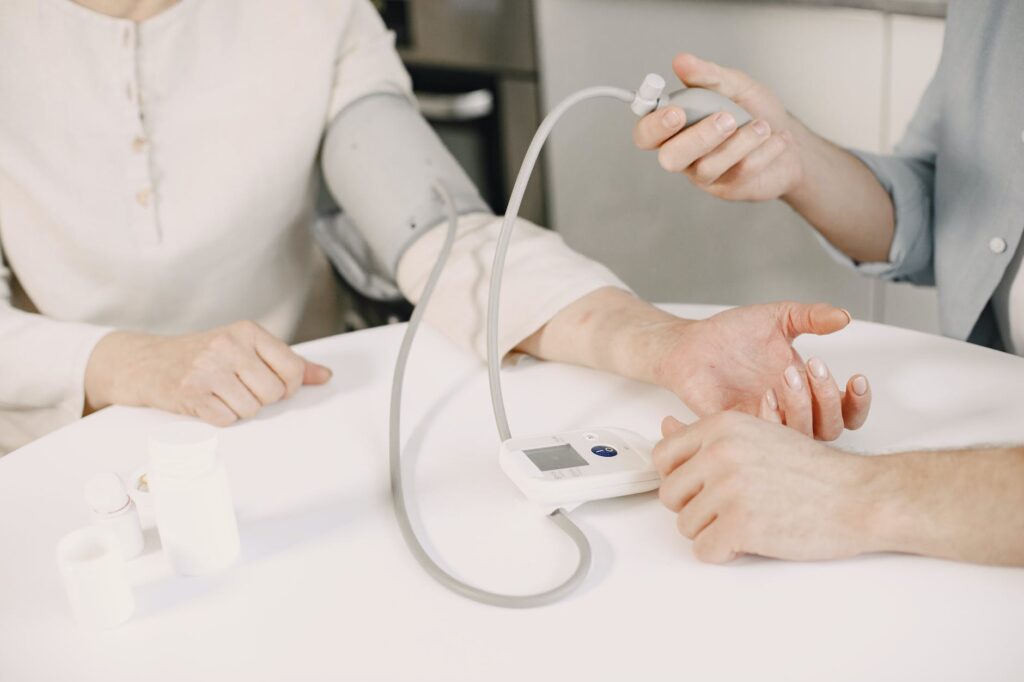
Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of your arteries. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) and is usually represented by two numbers, systolic and diastolic pressure. Hypertension is defined as having a blood pressure reading of 130/80 mm Hg or higher.
Long-Term Effects of Hypertension
If left untreated, hypertension can lead to numerous health complications over time, including:
- Heart Disease: High blood pressure forces the heart to work harder to pump blood throughout the body, leading to an increased risk of coronary artery disease, heart attack, and heart failure.
- Stroke: Hypertension contributes to the narrowing and hardening of arteries, which can lead to a clot or rupture of a blood vessel in the brain, causing a stroke.
- Kidney Damage: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste and excess fluid from the body. This can lead to chronic kidney disease or even kidney failure.
- Vision Loss: Hypertension can cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems or even blindness.
- Cognitive Decline: Long-term hypertension has been linked to cognitive decline, dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease, as it can negatively impact blood flow to the brain.
Stimulant Medications and Blood Pressure

Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) and amphetamines (Adderall, Vyvanse), are commonly prescribed to treat ADHD and other conditions. While they can be highly effective in managing symptoms, they may also have an impact on blood pressure.
Stimulant medications work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. This increase in neurotransmitters can lead to a temporary rise in blood pressure and heart rate. For most individuals, this increase is modest and may not pose significant health risks. However, for those with pre-existing hypertension or a predisposition to high blood pressure, the use of stimulant medications can potentially exacerbate the issue.
Possible Strategies to Manage Blood Pressure While on Stimulant Medications
If you are prescribed stimulant medications and have concerns about their potential impact on your blood pressure, consider the following strategies:
- Monitor Blood Pressure Regularly: Regularly checking your blood pressure is crucial for identifying any increases and managing your hypertension. It is essential to discuss your blood pressure readings with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthier lifestyle can help manage hypertension and minimize the potential impact of stimulant medications on blood pressure. This includes eating a balanced diet, reducing salt intake, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding tobacco products.
- Medication Adjustment: In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend adjusting the dosage or type of stimulant medication you are taking to minimize potential effects on blood pressure. They may also consider prescribing a non-stimulant alternative, such as atomoxetine (Strattera) or guanfacine (Intuniv), if appropriate for your condition.
- Hypertension Treatment: If your blood pressure remains elevated despite lifestyle changes and medication adjustments, your healthcare provider may recommend adding or adjusting medications specifically designed to treat hypertension.
Conclusion

Understanding the long-term effects of hypertension is essential for maintaining overall health and minimizing the risk of severe complications. While stimulant medications can potentially impact blood pressure, working closely with your healthcare provider and implementing the appropriate strategies can help manage both your blood pressure and the symptoms of your condition. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication or treatment plan, as they can guide you in making the best decisions for your individual needs.
It is essential to remember that each person’s experience with hypertension and stimulant medications may differ. Factors such as age, overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions can influence the impact of these medications on blood pressure. By staying informed and actively working with your healthcare team, you can ensure that you receive the most effective treatment while minimizing potential risks associated with hypertension and stimulant medications.
In summary, the long-term effects of hypertension can be severe, and stimulant medications may have an impact on blood pressure for some individuals. With careful monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, and open communication with your healthcare provider, it is possible to manage both hypertension and the symptoms of conditions that require stimulant medications. Prioritizing your health and well-being is vital, so don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns or questions you may have with your healthcare team.

